- Books & Media
- Print Books
- eBooks
- CourseReserves
- Loanable Technology
- DVDs
- CDs
- Databases
- A-Z Database List
- EBSCOhost Databases
- Articles (Search & Discover)
- State Journal-Register (NewsBank)
- Study Rooms
- Book a Study Room
Service Alert
Service Alert
As you go through this guide, remember that you are judging a webpage's quality by the criteria you establish. Just because a web page may be lacking in one criterion, doesn't mean the whole webpage is bad. The reverse is also true. Just because a web page meets some criteria, doesn't mean it is automatically a quality resource. You have to look at all of the established criteria and THEN decide if the website is good or bad based on your research need/research question.
Your home address tells a person where you live. It is made of your address number, street address, city, state, and zip code. Knowing all of these parts gives a person a cohesive picture as to information about where you live. Similarly, a web address tells people where the particular site lives on the internet through identifying information. Being able to decipher a web address, can aid in the first steps of understanding what you are looking at online.
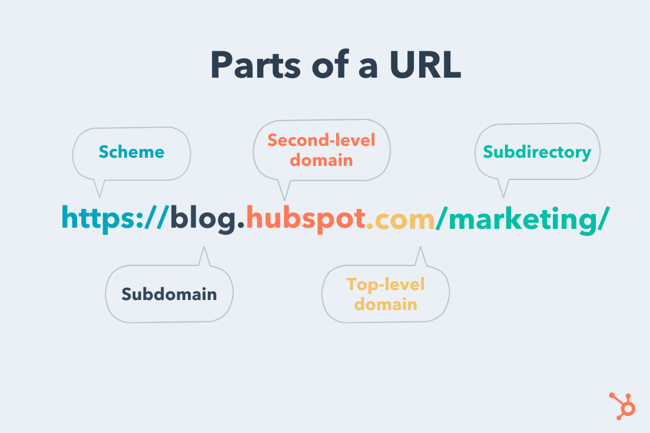
image credit: HubSpot https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/parts-url
Web Address Broken Down Further:
Scheme
HTTP or hypertext transfer protocol is the standard protocol used to share files on the internet
HTTPS or hypertext transfer protocol secure means that the website employs an SSL security certificate, which encrypts data between the user and the website. The added layer of security keeps a website from being hacked and personal information from being leaked.
image credit: Blue Anchor Digital Marketing https://blueanchordigital.com/http-vs-https/
Subdomain
A subdomain commonly exists to logically separate a website into sections. Examples: jobs.yoursite.com, FAQs.yoursite.com
A subdomain exists as an extension of the second-level domain--you cannot have a subdomain without the second-level domain--and they act as two separate websites with their own themes, functionalities, and look.
Other uses of subdomains
Creating a mobile version of a website creates better display functionality for its content on mobile devices (i.e. cell phones, tablets)
Example: m.yoursite.com
fr.yoursite.com (fr = French language version)
de.yoursite.com (de = German language version)
en.yoursite.com (en = English language version)
es.yoursite.com (es = Spanish language version)
Top-Level Domain
Often referred to as domain suffix or generically as domain. See more about Top-Level Domains, below.
Subdirectory
The subdirectory lets you know where on the website you are. The more subdirectory levels added to the web address the more deeply within the webpage you are embedded. Think of it like a bread crumb trail of how to get to where you want to be and how to get back to that specific spot again.
The domain name is an indicator of the sponsoring of a particular website.
Below are some of the most common top-level domains (often referred to as domain suffixes):

